Also see:
Estrogen, Uterine Fibroids, and Thyroid Nodules
Autoimmune Disease and Estrogen Connection
Hormonal profiles in women with breast cancer
PUFA Increases Estrogen
PUFA Inhibit Glucuronidation
PUFA Promote Cancer
Maternal PUFA Intake Increases Breast Cancer Risk in Female Offspring
Vitamin A: Anti-Cancer and Anti-Estrogen
Toxic Plant Estrogens
The Dire Effects of Estrogen Pollution
Progesterone: Essential to Your Well-Being
Alcohol Consumption – Estrogen and Progesterone In Women
Estrogen, Endotoxin, and Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury
Estrogen Levels Increase with Age
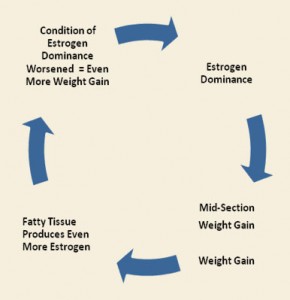
Fat Tissue and Aging – Increased Estrogen
Estrogen Related to Loss of Fat Free Mass with Aging
Bisphenol A (BPA), Estrogen, and Diabetes
Shock Increases Estrogen
“Early research had also shown that estrogen diminishes liver glycogen storage while progesterone increases both blood sugar and liver glycogen…Estrogen is also a promoter of insulin release and action, lowering blood sugar and promoting fat synthesis.” -Ray Peat, PhD
“With aging, the loss of glycogen in the brain has serious consequences, including insomnia. Estrogen’s depletion of glycogen in other tissues is probably important for their functioning, and thyroid and progesterone are known to help maintain the glycogen stores.” -Ray Peat, PhD
J Endocrinol September 1, 1974 62 439-449
SHORT-TERM EFFECTS OF OESTRADIOL BENZOATE IN NORMAL, HYPOPHYSECTOMIZED AND ALLOXAN-DIABETIC MALE RATS
M. N. GOODMAN and R. L. HAZELWOOD
Studies were undertaken to determine the effects and possible mode of action of 17β-oestradiol benzoate (OEB) in alloxan-diabetic male rats. Adlibitum or pair-fed normal, diabetic, and hypophysectomized rats received daily subcutaneous injections of 10 μg OEB for 10 days. In normal rats, OEB decreased plasma glucose, increased plasma immunoreactive insulin, growth hormone and corticosteroid levels, increased pancreatic β-cell granulation, and enhanced glucose stimulation of insulin release in vitro. In alloxan-diabetic rats, OEB treatment decreased urinary glucose excretion, increased plasma growth hormone and corticosteroid levels and slightly enlarged the pancreatic islets of Langerhans. In hypophysectomized rats, OEB decreased plasma glucose, increased plasma insulin levels, and slightly enlarged the pancreatic islets of Langerhans.
These results suggest that OEB affects experimental diabetes by a direct action on the pancreas, promoting insulin formation, and possibly by an indirect action mediated through hypophysial secretions.